The Greatest Guide To Dementia Fall Risk
The Greatest Guide To Dementia Fall Risk
Blog Article
The 20-Second Trick For Dementia Fall Risk
Table of ContentsSome Known Factual Statements About Dementia Fall Risk Some Known Questions About Dementia Fall Risk.The 5-Second Trick For Dementia Fall RiskFacts About Dementia Fall Risk Uncovered
An autumn threat evaluation checks to see how likely it is that you will certainly fall. It is primarily provided for older adults. The assessment normally consists of: This consists of a collection of questions concerning your overall wellness and if you have actually had previous drops or troubles with balance, standing, and/or walking. These tools check your toughness, balance, and gait (the way you walk).Interventions are recommendations that might lower your danger of falling. STEADI includes 3 steps: you for your risk of dropping for your threat aspects that can be enhanced to attempt to avoid drops (for instance, balance troubles, impaired vision) to reduce your threat of falling by using reliable methods (for example, providing education and learning and sources), you may be asked several questions consisting of: Have you fallen in the previous year? Are you worried about dropping?
If it takes you 12 secs or more, it might suggest you are at greater risk for a loss. This examination checks strength and equilibrium.
The positions will obtain more challenging as you go. Stand with your feet side-by-side. Relocate one foot midway ahead, so the instep is touching the big toe of your various other foot. Move one foot fully before the various other, so the toes are touching the heel of your various other foot.
What Does Dementia Fall Risk Do?
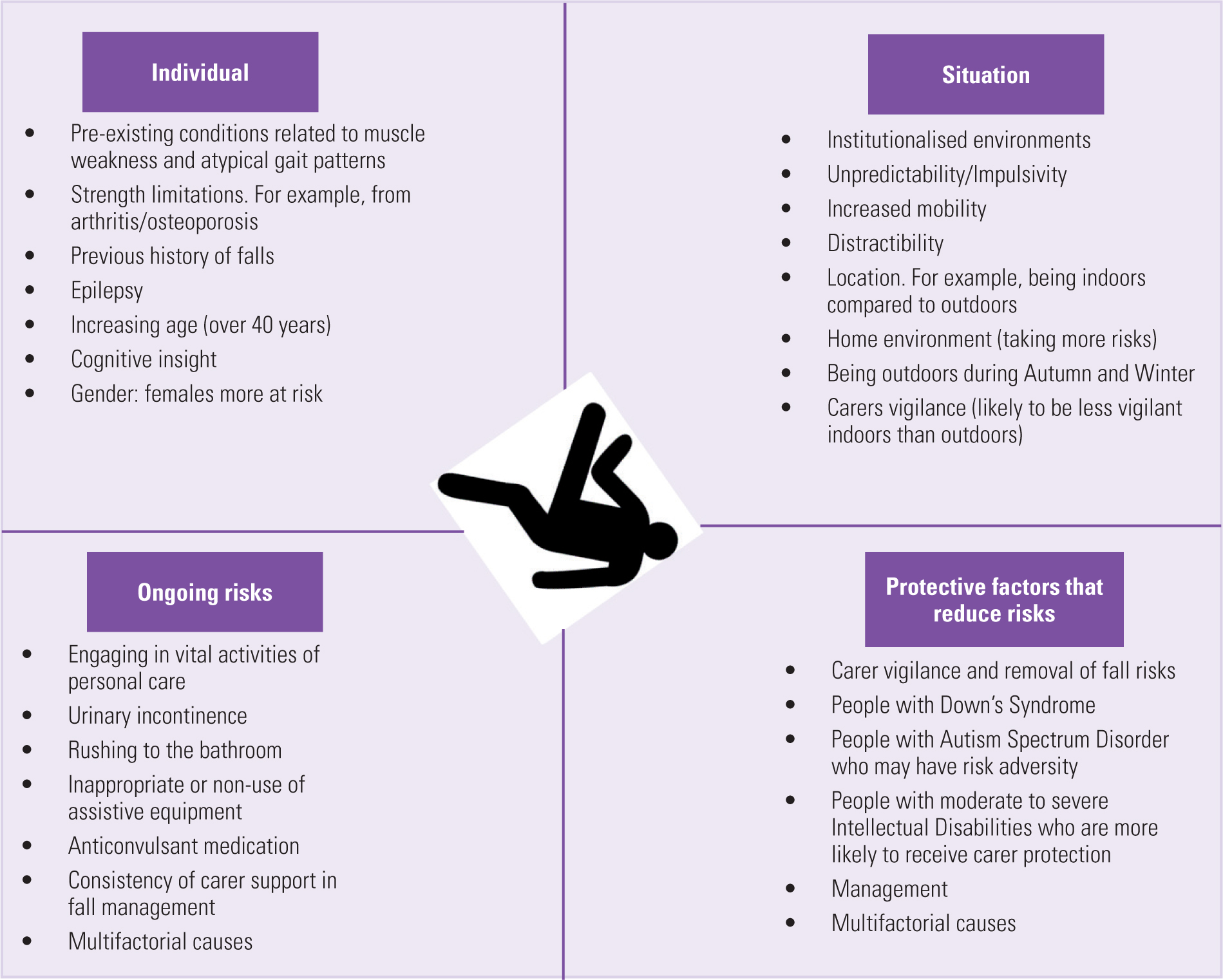
Many falls happen as an outcome of several adding aspects; as a result, handling the threat of falling starts with determining the aspects that contribute to drop threat - Dementia Fall Risk. Several of the most pertinent threat aspects include: History of prior fallsChronic medical conditionsAcute illnessImpaired gait and balance, lower extremity weaknessCognitive impairmentChanges in visionCertain risky drugs and polypharmacyEnvironmental aspects can additionally raise the risk for drops, including: Inadequate lightingUneven or damaged flooringWet or unsafe floorsMissing or harmed handrails and get hold of barsDamaged or incorrectly equipped devices, such as beds, mobility devices, or walkersImproper use assistive devicesInadequate guidance of individuals residing in the NF, consisting of those who exhibit hostile behaviorsA effective autumn danger management program needs a comprehensive professional assessment, with input from all participants of the interdisciplinary group

The care plan should also include treatments that are system-based, such as those that advertise a risk-free environment (suitable lights, handrails, get hold of bars, etc). The performance of the interventions must be assessed occasionally, and the care plan modified as necessary to show changes in the autumn threat evaluation. Implementing an autumn risk administration system using evidence-based finest technique can decrease the occurrence of drops in the NF, while restricting the potential for fall-related injuries.
What Does Dementia Fall Risk Mean?
The AGS/BGS guideline recommends screening all adults aged 65 years and older for fall risk yearly. This screening contains asking clients whether they have fallen 2 or more times in the past year or sought medical attention for a fall, or, if they have not fallen, whether they feel unsteady when walking.
Individuals who have dropped as soon as without injury should have their equilibrium and stride assessed; those with stride or equilibrium irregularities ought to get added evaluation. A history of 1 Going Here loss without injury and without stride or equilibrium troubles does not require further assessment past ongoing annual fall threat testing. Dementia Fall Risk. A loss threat analysis is needed as part of the Welcome to Medicare this article evaluation
7 Simple Techniques For Dementia Fall Risk
Documenting a falls background is one of the top quality indicators for loss prevention and monitoring. copyright medications in specific are independent predictors of drops.
Postural hypotension can frequently be relieved by lowering the dosage of blood pressurelowering drugs and/or quiting medicines that have orthostatic hypotension as an adverse effects. Use above-the-knee assistance pipe and copulating the head of the bed boosted might likewise lower postural decreases in high blood pressure. The preferred aspects of a fall-focused physical exam are displayed in Box 1.

A pull time higher than or equivalent to 12 secs recommends high fall threat. The 30-Second Chair Stand test assesses lower extremity stamina and equilibrium. Being unable to stand from a chair of knee height without utilizing one's arms shows increased loss danger. The 4-Stage Equilibrium test examines fixed equilibrium by having the patient stand in 4 placements, each considerably a lot more tough.
Report this page